Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 6 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2019-06-30 Origin: Site








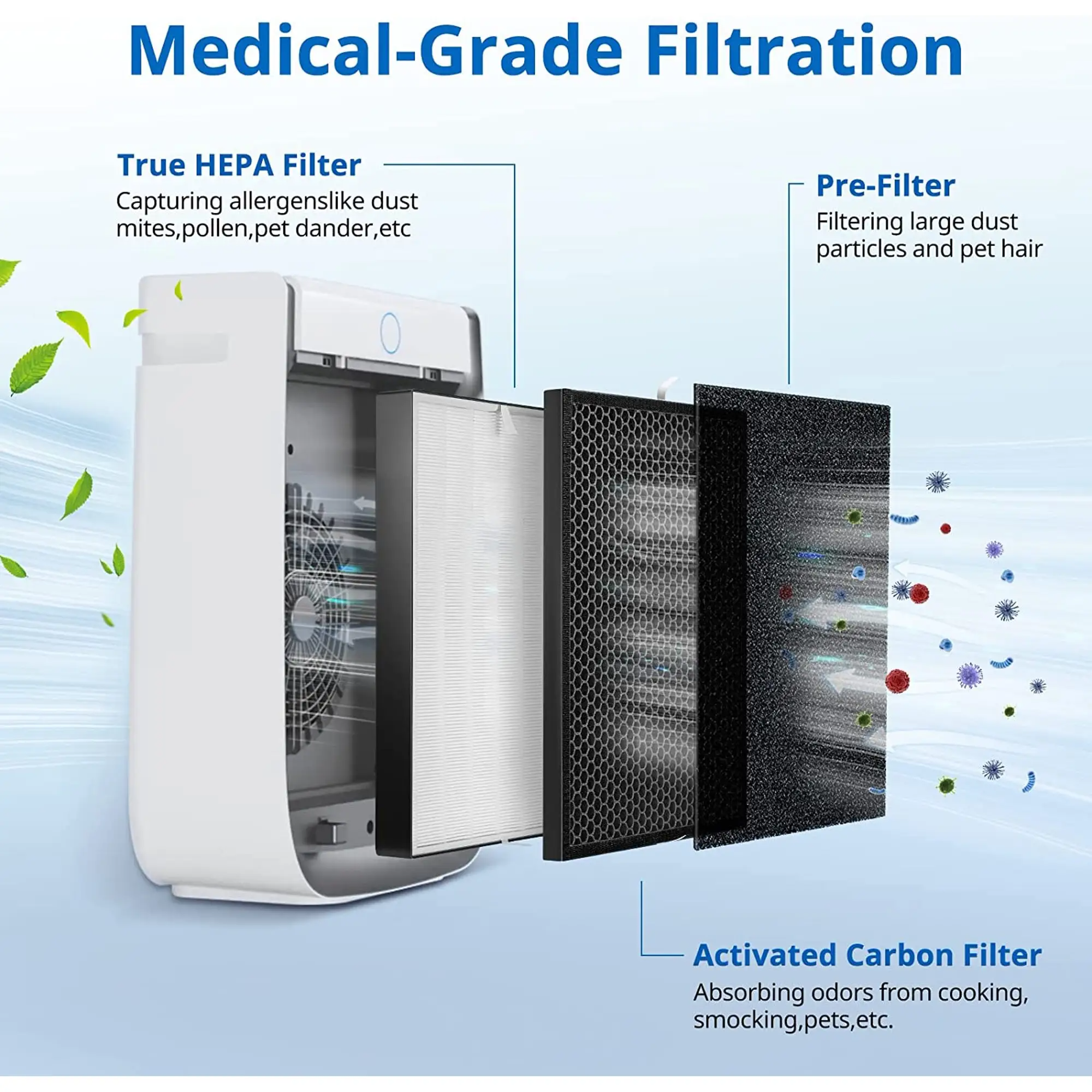
A true hepa filter can capture 99.97 percent of dust particles with a diameter of 0.3 microns (1 micron is a millionth of a meter).Particles 0.3 microns in diameter are not particularly important: they are only most likely to pass through filters, where larger and smaller particles are more efficiently trapped.From a 0.3 micron perspective, it's worth remembering that the average human hair is about 50 to 150 microns across, so hepa filters can remove dust hundreds of times thinner than hair.The coarse soot particles from diesel exhaust are commonly referred to as PM10(particles smaller than 10 microns) or PM2.5(particles smaller than 2.5 microns), so you can see that HEPA filters work at least 10 times smaller than PM10.Real hepa filters are more sanitary than regular ones because they block mold spores and even some bacteria and viruses.It's clean on the micro scale.
When it comes to filters for breathing equipment, NIOSH identifies nine different levels based on three different efficiency levels (95, 99, and 99.97%) and three filter resistance degradation levels (R N, P).N for oil intolerance, R for oil intolerance, P for oil intolerance.Therefore, you might see a filter labeled N95(95% efficiency and oil resistance) or P100(99.97% efficiency and oil resistance).
You may also see HEPA filters classified using the five letters A through E, based on their ability to capture particles and resist airflow.Type A is the least effective one that still meets basic HEPA standards, while type E (on the other end of the scale) is A military-grade filter capable of handling chemical, radioactive or biological particles.There is also a classification depending on whether the filter is fireproof (type 1) or semi-combustible (type 2).
Even if you have allergies, these categories don't make much sense if you just buy a simple air purifier or vacuum cleaner.For most people, the key is to make sure the product you buy has a real hepa filter (remember, 99.97% of 0.3 micron particles are real hepa particles, often referred to as "real hepa" or "absolute hepa").Avoid vague, meaningless descriptions by manufacturers, such as "like hepa" and "hepa type", without any quantification.A true HEPA filter always references these Numbers.Some professional-grade vacuums will have extra mechanisms to process particles even smaller than 0.3 microns, such as activated carbon particles (similar to those found in water filters).Finally, if you need industrial-strength air purification, there is a more stringent standard called ULPA, which can capture 99.99% of particles larger than 0.12 micron.
Knowing how filters work comes in handy when deciding what to buy.A vacuum with an appropriate hepa filter channels almost all (over 90%) of the dirty air into the filter;If it doesn't, it just rearranges the dirty air.Hepa filters prevent air from passing through vacuum cleaners: it takes a lot of suction to pull air out of the tangled fibers.This is why true hepa vacuum requires a more powerful engine and low power may not clean effectively.For the same reason, air purifiers that use hepa filters may be more energy efficient (which means they run longer and are noisier, while competitors work differently, such as photocatalysis).Hepa filters also need to be cleaned or replaced regularly (which will increase operating costs);Before submitting, you may want to check the cost of replacing the filter.
The Importance of Replacing Your Air Purifier Filters in Spring
Are There Any Differences between Third-party Filters And Original Filters?
The difference between rated air volume and standard air volume of high efficiency air filters
Breathe Fresher Air: A Guide To The Role And Replacement of Air Purifier Filters